Alcohols
WHAT ARE ALCOHOLS?
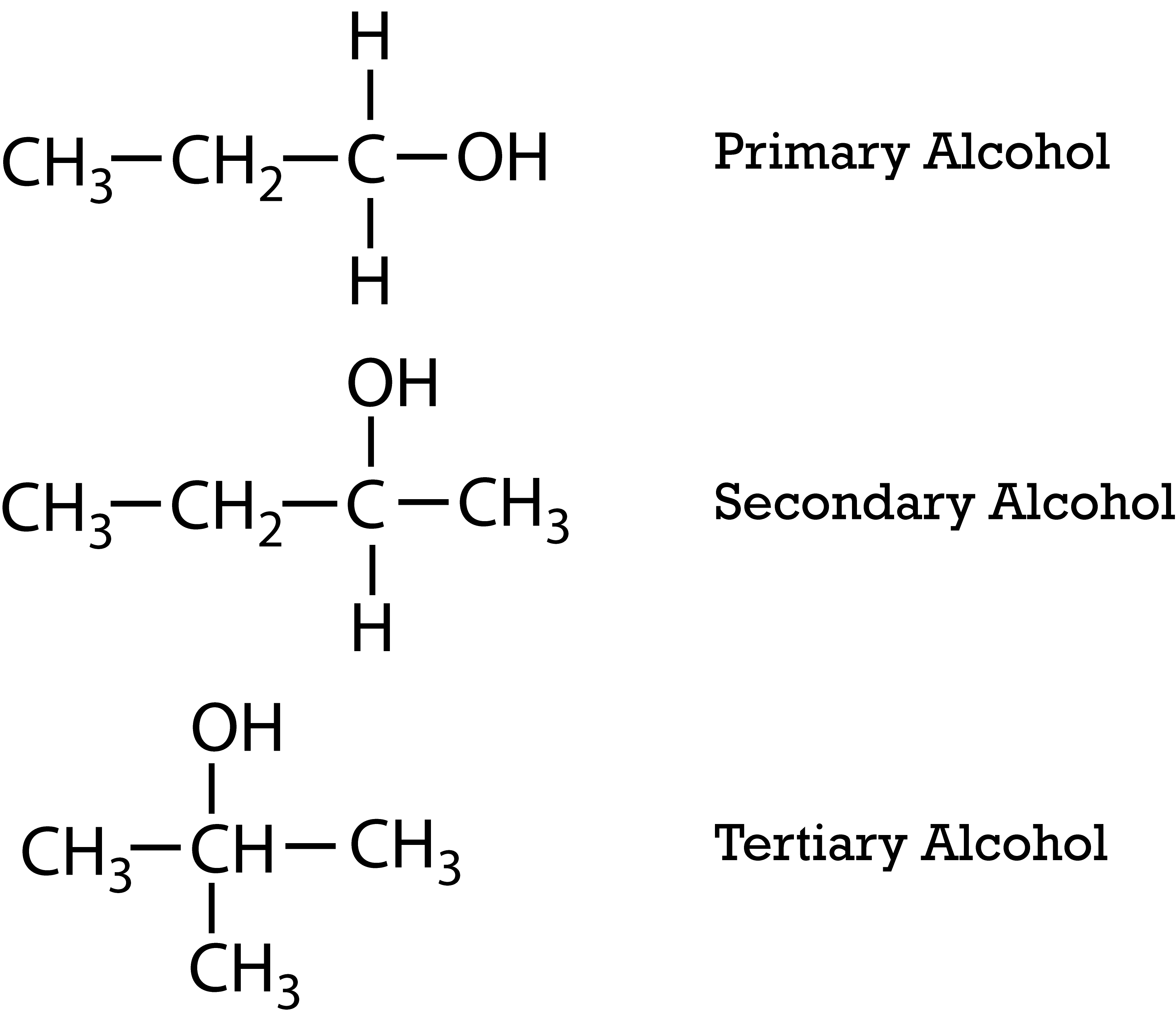
Alcohols are carbon-based compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms in an alkane have been replaced by an -OH group. They can be “primary alcohols” (if the carbon which carries the -OH group is only attached to one alkyl group.), “secondary alcohols” (if the carbon with the -OH group attached is joined directly to two alkyl groups) or “tertiary alcohols” (if the carbon atom holding the -OH group is attached directly to three alkyl groups). The length of the chain affect their boiling point, as larger chains require more energy to break their bonds. Moreover, alcohols have higher boiling points than their alkanes. In addition, they are very soluble in water, particularly shorter chains, because of the effect of the –OH group that is strongly attracted to water molecules.
HOW ARE THEY PRODUCED?
A way of producing alcohols is through fermentation. This is the process in which yeast breaks down sugar to create energy for anaerobic respiration. In other words, sugar transforms into alcohol and carbon dioxide, which goes into the air, leaving ethanol and water. (Glucose + yeast -> alcohol + carbon dioxide). To successfully produce this method we need a temperature of approximately 37°C and an optimum pH. Moreover, another way of getting alcohol is hydrating alkenes,this means, adding water to the double‐bonded carbons.
WHAT DO THEY PRODUCE IN OUR ORGANISMS?
Unlike food, alcohol travels easily through our body and about 20% of the alcohol that we consume is absorbed immediately into our bloodstream. The most known and common effect of alcohol is happiness and the feeling of less inhibition, however inside, our bodies suffer and may get serious consequences.
Some effects include...
- Brain: it interferes with the brain’s communication pathways, and can affect the way the brain looks and works. These disruptions can change mood and behaviour, and make it harder to think clearly, our visions turn blurry and we may lose coordination.
- Heart: Some diseases produced by alcohol in our hearts include Cardiomyopathy, Arrhythmias, Stroke, High blood pressure. However, researches show that consume moderated amounts of alcohol may help with coronary heart diseases in old people.
- Liver: On average, it takes the liver about one hour to break down one unit of alcohol. Its effects include: Steatosis, or fatty liver, Alcoholic hepatitis, Fibrosis and Cirrhosis.
- Pancreas: Alcohol causes the pancreas to produce toxic substances that can eventually lead to pancreatitis, a dangerous inflammation and swelling of the blood vessels in the pancreas that prevents proper digestion.
- Cancer: Alcohol increases the risk of developing cancers such as cancers of the mouth, esophagus, liver, breasts and throat.
- Immune System: Drinking too much can weaken your immune system, making your body a much easier target for disease.
Below, i will share with you a video explaining the effects of alcohol particularly in teenagers. Nowadays, people are entering the world of alcohol at a younger age, without even knowing what they are putting into their organisms; therefore i believe it is essentials this things are taught in class.
The effects of alcohol depend on...
- Size/weight: People who are smaller and weigh less will feel the effects of alcohol more quickly because they have less tissue to absorb it.
- Whether or not you've eaten: Food slows down the rate of absorption, however the effects won't vary.
- Type of drink: Alcohol mixed with water or fruit juice is absorbed more slowly, while fizzy drinks or mixers speed up the absorption process.
- Age: Younger people tend to be smaller, weigh less and less experienced in dealing with the effects of alcohol. It will therefore have a greater effect on them and do more damage than it would to an older person. Alcohol can be particularly damaging to teenage brains, which are still developing. As people get older, changes such as increased body fat and decreased body water content affect how alcohol is processed by the body, making older people more susceptible to the effects of alcohol.
- Gender: Women are more affected than men. The reason for this is that women are smaller and weight-less than men, and have less tissue to absorb alcohol.Women's bodies are made up of more fat and less water than men's. So if a man and a woman are the same size and drink the same amount, the alcohol is stronger in the woman's blood than in the man’s and she will get drunk more quickly and feel the effects for longer. Women have lower levels of the enzyme that breaks down alcohol, so alcohol will stay in their system longer and have a greater effect.Women also feel the effects of alcohol more quickly than normal just before a period and during ovulation. The contraceptive pill can have the opposite effect – it takes longer for the alcohol to leave the body and a woman may drink more than she realises before she feels the effects.
The alcohol we consume takes half an hour to reach its highest level. 90% of alcohol is broken down in the liver camera while the rest of it is passed out of the body in urine and your exhaled breath. Therefore, alcohol test are necessary to measure whether you are legally drunk or not. There are different types of alcohol test, for instance, it can be a blood test, but you need to make sure you haven't had any medicines before. Another type of test are the breath tests, which involve blowing (exhaling) into a glass tube, or the the saliva test, which requires that you saturate the test strip inside with saliva. This tests use the BAC (Blood alcohol content, blood alcohol concentration, blood ethanol concentration, or blood alcohol level) that is used as a metric of alcohol intoxication for legal or medical purposes. It is expressed as a percentage of ethanol in the blood in units of mass of alcohol per volume of blood or mass of alcohol per mass of blood, depending on the country.


Comentarios
Publicar un comentario